Web Design II
Class 07: WordPress Theme SetupTopics
- Themes
- Basic PHP
- Templates
- Functions
- Week 07 Custom Theme Site (theme setup) Lab

Welcome to class 007
Themes
Theme Explanation:
WordPress is a CMS (content management system) and the theme dictates how that content is to be displayed. It is meant to control the visual aspects (design) of the site and not functionality, although typically some is included as well. Plug-ins are meant to add functionality specifically.
Theme Contents:
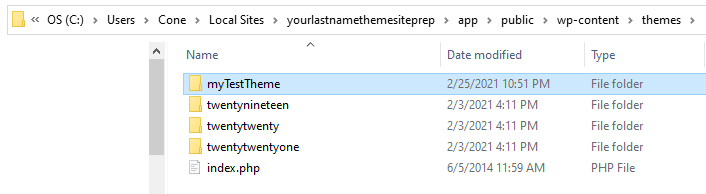
A theme is a collection of files with specific formatting that work together to form the presentation of the site.
Theme files can be categorized:
- Templates
- These are the shells of the displayed pages. Similar to HTML layouts for different pages.
- Design
- Things concerned with the overall design like CSS and some JavaScript.
- Function
- More complex behaviors of the theme that directs operations.
A theme contains:
- Required
- index.php
- The fallback template for all pages. The basic formatting.
- style.css
- The general design document like in a hard-coded site.
- index.php
- Typical
- header.php
- The partial template for the heading of the page that is called at the top of each page.
- footer.php
- The partial template for the footer of each page called at the bottom.
- functions.php
- Contains all the PHP functions that add functionality. Some call it the plug-in of the theme (though you shouldn’t call it that).
- page.php
- The template for your the pages of your site (go figure!).
- screenshot.jpg (1200 x 900)
- An image that represents the theme inside WordPress.
- header.php
- Others
- Many others are often included. Templates for other pages such as posts, 404, search, etc. Other design documents like CSS, JavaScript to apply design, animation, responsive elements etc. Php documents to incorporate more complex function.

Basic PHP
PHP (hypertext preprocessor):
PHP is an open-source scripting language that is executed by the server. It allows you to write dynamic functions inline with HTML. PHP is used to write the most basic WordPress site as well as the something as complex as Facebook.
Syntax:
PHP is an OOP (object oriented programming) language. This means it may contain variables, loops, functions, etc. like other robust programming. It will run somewhat like JavasScript.
Let’s look at some basic examples:
Start/End:
A PHP document normaly contains html. As such you, must have tags much like HTML that so that it is apparent when code should be read as PHP.
<?php echo "<h1>Check out PHP</h1>"; ?>
<p>written alongside HTML</p>
<?php echo "<h2>and back into PHP</h2>"; ?>Variables:
The variables in PHP are simple to create. They do not need to be explicitly declared.
- $
- variable names should start with this symbol
- =
- the assignment
- ” “
- the value assigned to the variable should be in quotes
<?php
$name = "Cone";
$age = "37";
?>Conditional Statements:
These test a comparison and will proceed with instructions based on it being true or false.
- if
- initial condition and state “if”
- ()
- test if statement inside parenthesis is true
- {}
- complete code inside brackets
- else
- if the statement in the parenthesis is not true
- {}
- complete code inside brackets
<?php
$t = date("H");
if ($t < "20") {
echo "Have a good day!";
} else {
echo "Have a good night!";
}
?><?php
$a = 4;
if($a < 5):
echo "Less than five";
else:
echo "Greater than five";
endif;
?>PHP may also use an “if():” “/endif;” structure. It works the same as the traditional method but uses a different syntax.
Loops
Runs code for as long as a tested condition is true. The while loop is used extensively in WordPress PHP.
- While
- initial condition and state “while”
- ()
- test if statement inside parenthesis is true
- {}
- repeatedly complete code inside brackets “while” the condition is true
<?php
$x = 1;
while($x <= 5) {
echo "The number is: $x <br>";
$x++;
}
?>Functions
A function is a block of code that may be run whenever it is called.
- function
- keyword stating it is function, followed by the function name
- ()
- parameters that will contain any variables sent to the function. These are called arguments when the function is called
- {}
- code contained inside the function that is run when called are placed inside the brackets
<?php
function writeMsg() {
echo "Hello world!";
}
writeMsg(); // call the function
?>Calling Functions
You may create your own function and call it like the example above. However, there are functions built-in to WordPress PHP that you will utilize often.
PHP is a loosely written language. This means that the syntax is often not strict. You will often see code that does the same thing written differently from one document to another. Be aware that you cannot mix syntaxes generally.
<?php
//writes to the browser
echo "<p>here is something written</p>";
//loads the content of a page
the_content();
//loads the stylesheet in the root folder
wp_enqueue_style('main_styles', get_stylesheet_uri());
?>There are a ton of built-in functions you can call, too many to list here. Notice that they start with a letter or number, no caps necessary, use ‘_’ in the name as oppose to camel-case, and don’t necessarily use ‘()’ arguments when called.
Templates
Templates:
Put simply, templates are the shell of the page design that the user of the theme will place their content into. There are a lot of templates you can create for your site but they are not required. They follow a template heirarchy.

In the template heirarchy index.php is the fallback template but you can see you create more and more specific templates for different layouts.
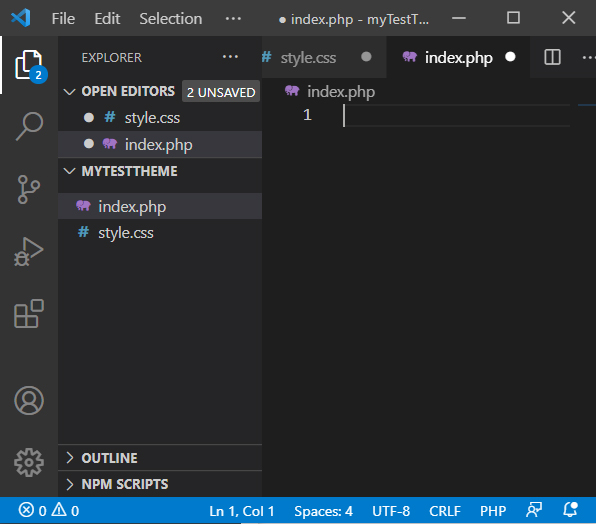
index.php:
The index.php is the fallback template for all posts (pages). As such this is the first php document to make.
- <?php
- the open tag to enter PHP mode
- wp_head();
- is a hook for WordPress to enter any function that is entered in the head of the page
- if ( have_posts() ) :
- tells the next block code to run if there is a post (or page)
- while ( have_posts() ) : the post();
- will run the following block of code as long as there are posts (or pages)
- the_title();
- writes the title of the page into the browser
- the_content();
- writes the content of the page into the browser
- endwhile;
- where the while loop block ends
- endif;
- where the if statement block ends
- wp_footer();
- is a hook for WordPress to enter any function that is entered in the footer of the page
- ?>
- closing tag of PHP
<?php
wp_head();
if ( have_posts() ) :
while ( have_posts() ) : the_post();
the_title();
the_content();
endwhile;
endif;
wp_footer();
?>This is the most fundamental code to be written in the index.php. It may be more robust.
This code uses “The Loop” inside it. This is a famous loop used often inside WordPress.
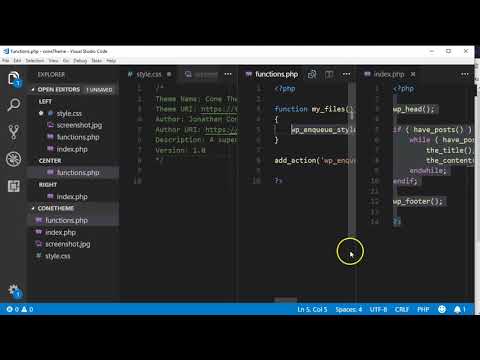
Functions
- <?php
- the open tag to enter PHP mode
- function my_files() {
- a function we created that we will be able to call in a later line of code in this document
- wp_enqueue_style(‘main_styles’, get_stylesheet_uri());
- load a stylesheet at the main directory where the main stylesheet exist
- wp_enqueue_style(‘my_responsive_style’, get_template_directory_uri() . ‘/css/responsiveStyle.css’);}
- load the responsiveStyle.css sheet in the css folder in the theme directory
- add_action(‘wp_enqueue_scripts’, ‘my_files’);
- this is the “hook” of the function. It tells it to run when WordPress loads the scripts
- ?>
- closing tag of PHP
<?php
function my_files() {
wp_enqueue_style('main_styles', get_stylesheet_uri());
wp_enqueue_style('my_responsive_style', get_template_directory_uri() . '/css/responsiveStyle.css');
}
add_action('wp_enqueue_scripts', 'my_files');
?>This will load the main stylesheet as well as a secondary one that contains the responsive code we created earlier
/*
Theme Name: MyTheme
Theme URI: https://teachmecone.flywheelsites.com
Author: cone
Author URI: https://teachmecone.flywheelsites.com
Description: A super simple theme
Version: 1.0
*/A comment with the above content should be placed inside the style.css document. Later various CSS rules will be added to properly format the design of the theme.
Class 07 Custom Theme Site (theme setup) Lab
Custom Theme Site (theme setup) Lab
In this lab you will develop the bones of your custom theme. HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and PHP will be produced.
You will be graded on the following:
- Lab Requirements
-
Techniques and processes covered in the instructional material is followed and implemented.
-
- Creativity & Craftsmanship
-
Excellent design choices, novel & appealing, and solid clean caliber work.
-
Resources:
- Assignment Video Tutorials
- You may watch these tutorial videos below to help you complete your assignment.
Lab Tutorial Slideshow
This tutorial will review WordPress as well as setup a site to apply our future custom theme to.
Wait! Before you go!
Did you remember to?
- Read through this webpage
- Watch the videos
- Submit Class 07 Custom Theme Site (theme setup) Lab on Blackboard