Introduction to 3D Modeling and Animation
Class 04: TopologyTopics
- Topology
- Deformation
- Basic Sculpting
- Week 04 Character Head Model Lab

This is class fore!
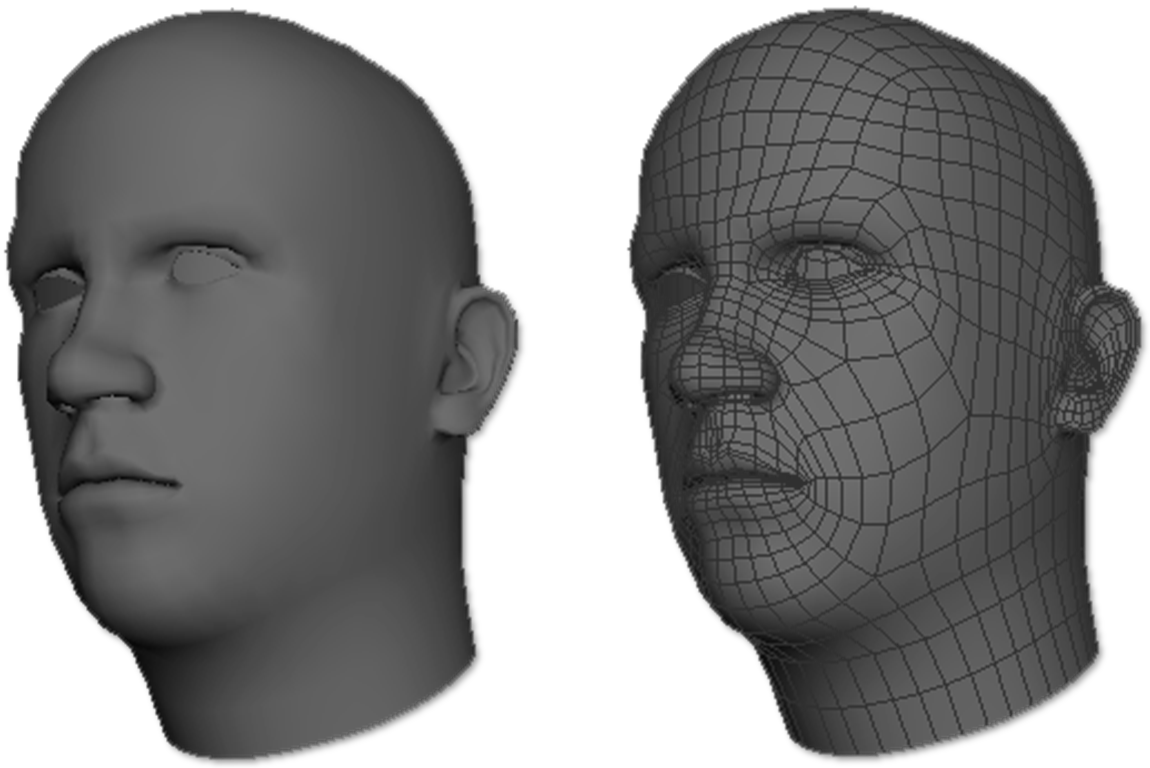
Topology
Topology
Topology refers to the geometric surface characteristics of a 3D object. Good topology support the three-dimensional form and ample deformation.

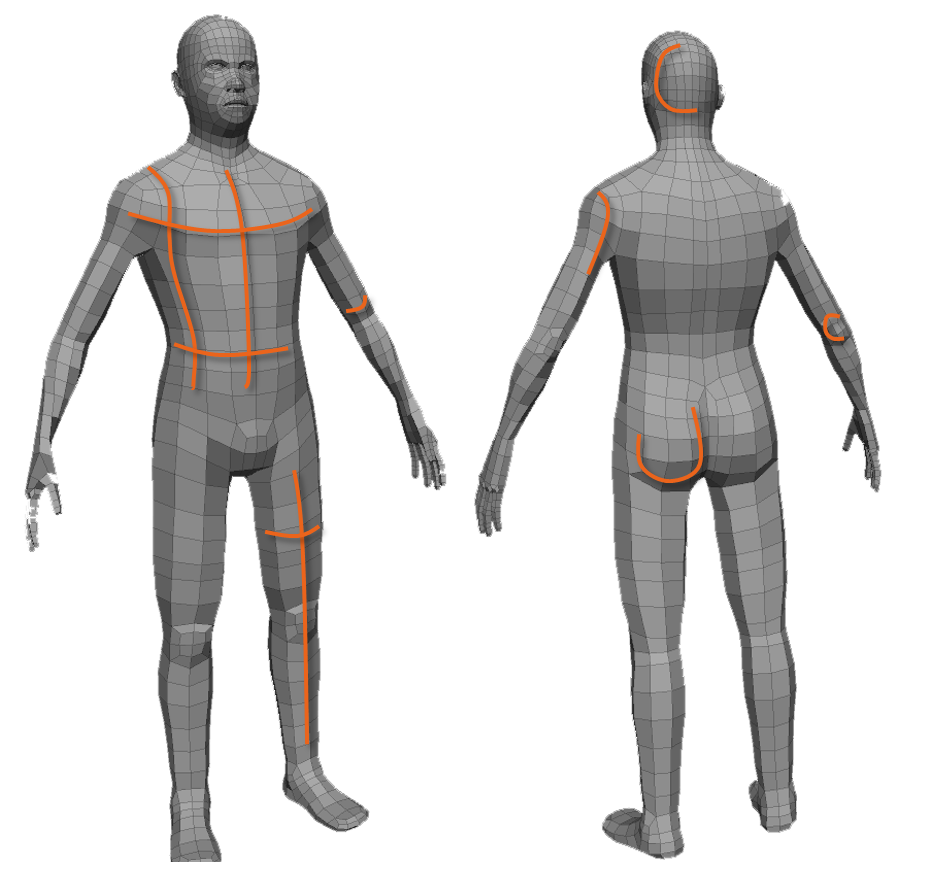
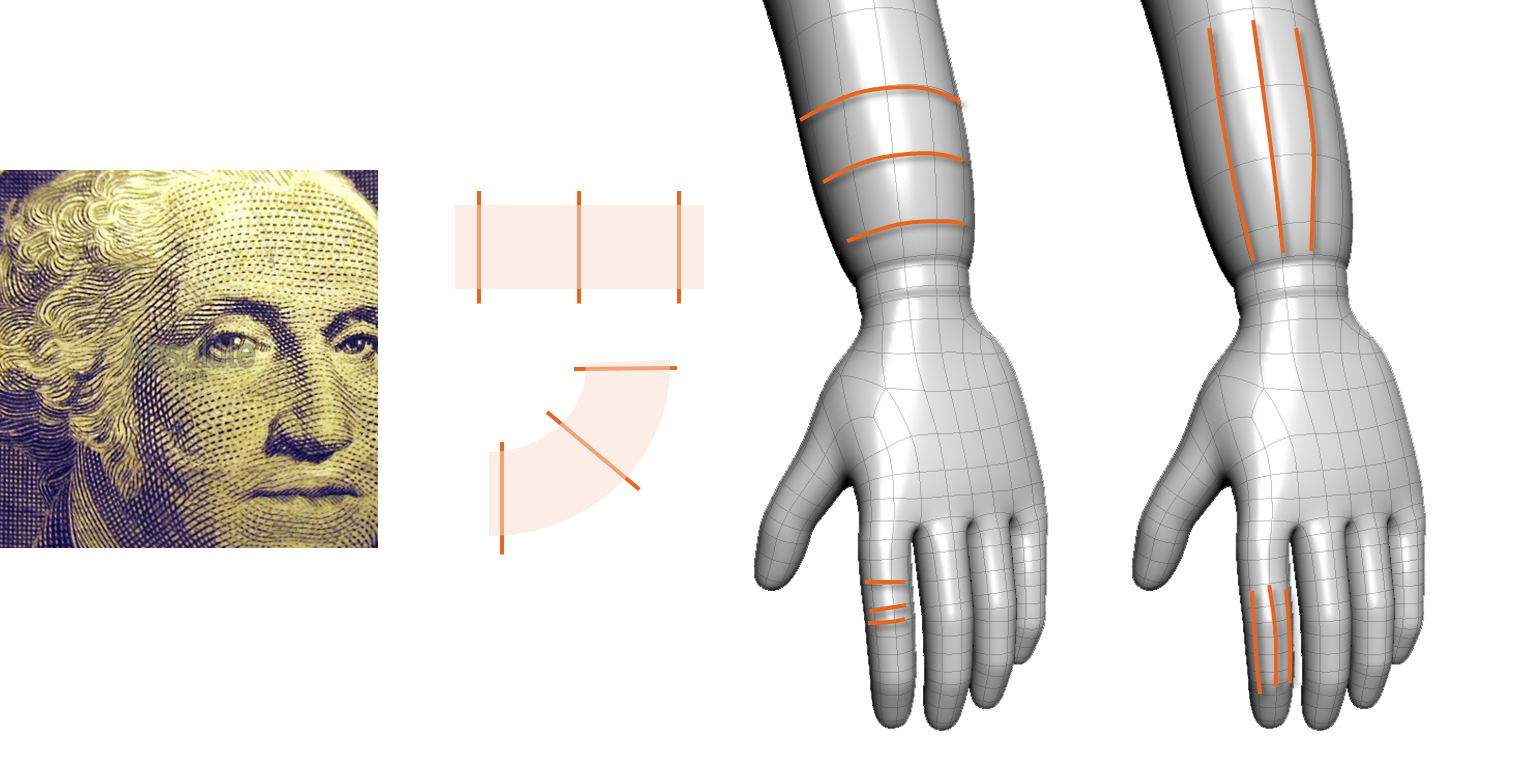
Deformation
Deformation
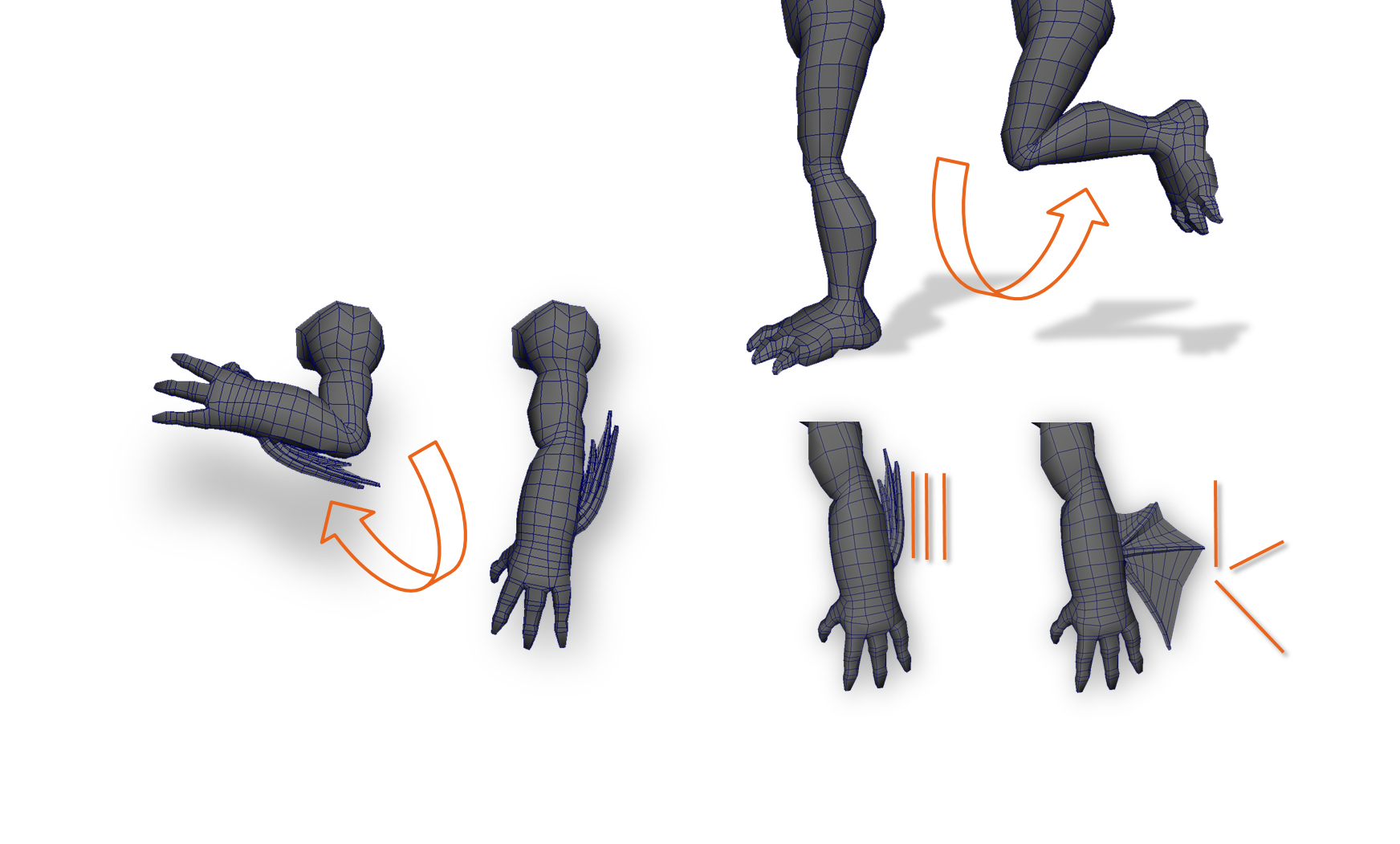
Deformation in a model refers to its ability to distort its shape. You must model your character to be able to bend, flex, twist, and so on depending on the areas of articulation.
Common Geometrical Errors
Non-Manifold Geometry
Non-manifold topology polygons have a configuration that cannot be unfolded into a continuous flat piece. Some tools and actions in Maya cannot work properly with non-manifold geometry. For example, the Boolean operations and the Reduce feature do not work with non-manifold polygon topology. The image below shows three examples of non-manifold topology polygons.

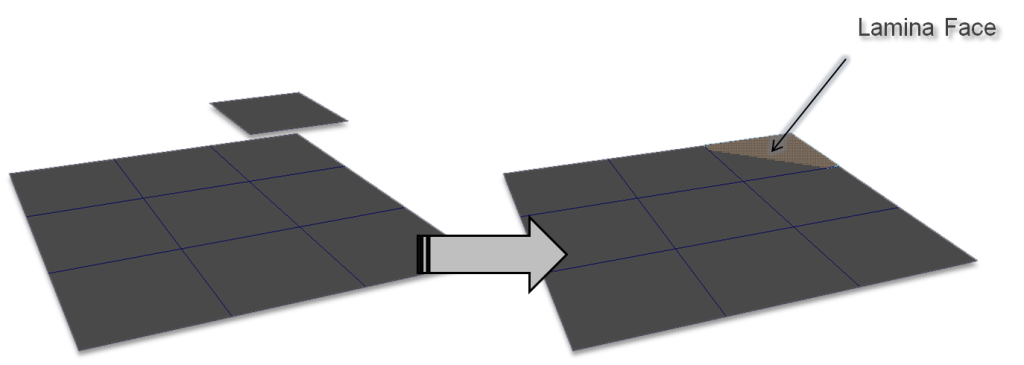
Lamina Faces
Lamina faces share all of their edges. Basically, one face “on top” of the other, usually sharing edges.
One common cause is extruding faces but not translating them after.
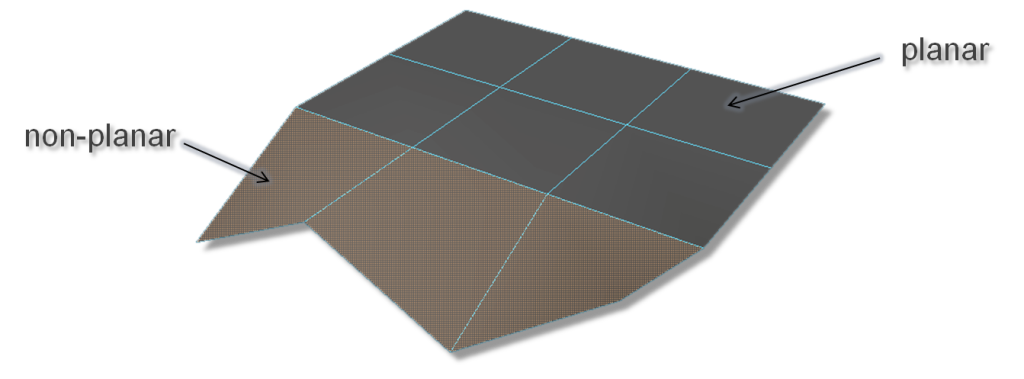
Non-Planar Surfaces
A polygon face is planar when all of its vertices lie in a certain plane. For example, a triangle face is always planar, because its three points define a plane.
A polygon face is non-planar when it has more than three vertices, and one or more of those vertices do not lie in the same plane. When a polygon mesh is comprised of quads or n-gons it is possible to have non-planar polygon faces.
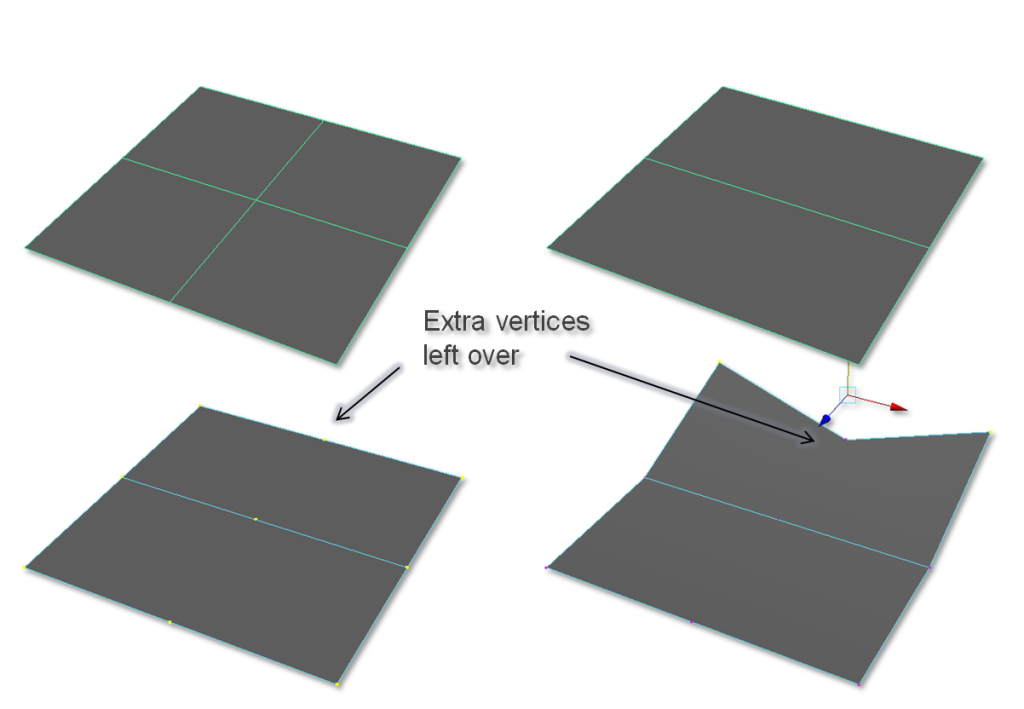
Floating Vertices
Be careful about have random floating vertices.
Deleting edges but not the vertices are a common mistake.
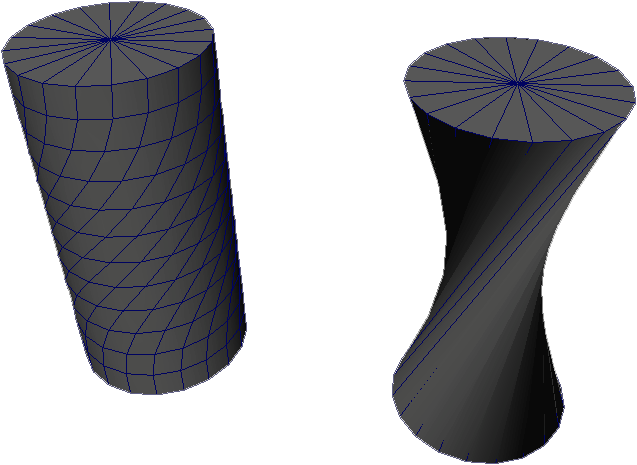
Poles/Stars
Poles are areas where more than four edges meet and result in poor contiguous surfaces.
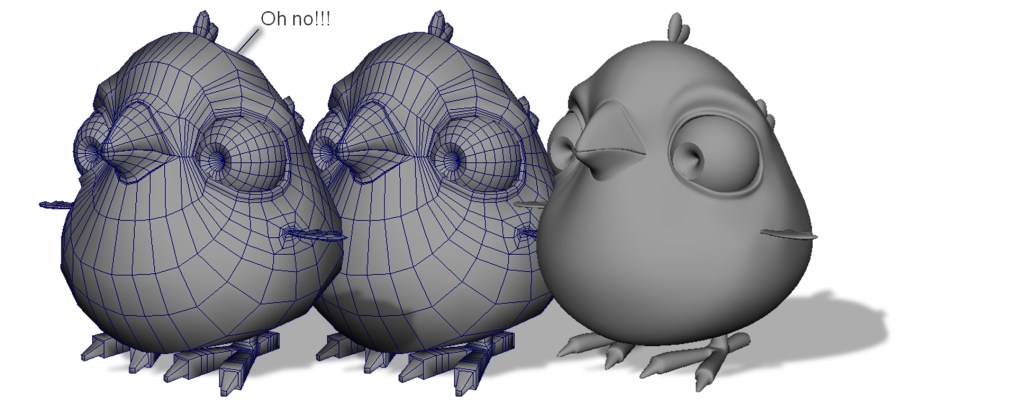
Dense or Sparse Geometry
Your objects should only have the necessary about of geometry needed to complete the form.

Non-Contour
If the geometry does not “wrap around the surface it will look incorrect and not deform appropriately.
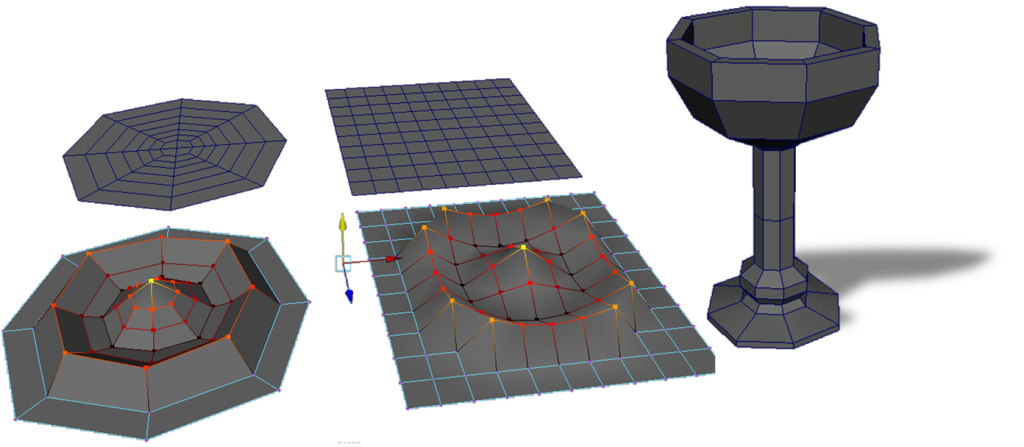
Non Square
You are looking for square geometry where possible.
Square geometry will model, texture, and deform better than non-square geometry.
That being said you also want to limit your total polycount.
Basic Sculpting
The window to the right shows a good example of a mechanical hard-surface model vs an organic soft-surface model.
Zbrush Core Mini
Pixologic Zbrush has become an industry standard in digital sculpting. It is however a paid program. It is also very complicated (not as much as Maya but still pretty bad). Pixologic offers a free “lower-grade” version of their program called, Zbrush Core Mini. It does not have all the bells and whistles but does allow for Dynamesh Sculpt.
Dynamesh is process of sculpting on a mesh and the model auto-generates the geometry necessary for the change to the surface to happen. Basically it automatically will subdivide the model as you sculpt. This is very free-form and you do not need to worry about the geometry of the model at all while you work, just the aesthetics of the form.
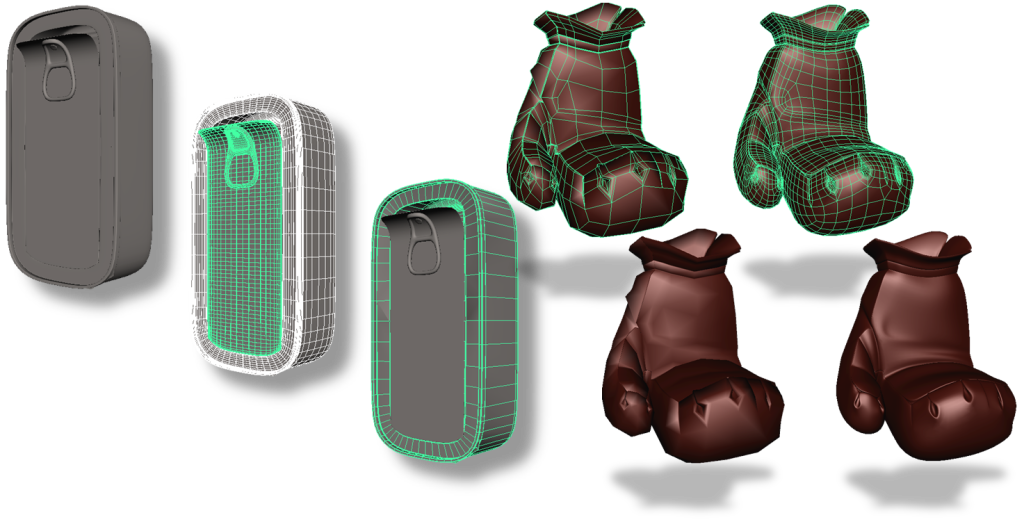
Retopology
Retopology is the process of creating a model with proper grid-flow on top of a reference model with poor geometry. This allows you to create an aesthetically pleasing model without concern of the geometry itself. Then you can simply use it as a guide to create a similar form but with proper topology.
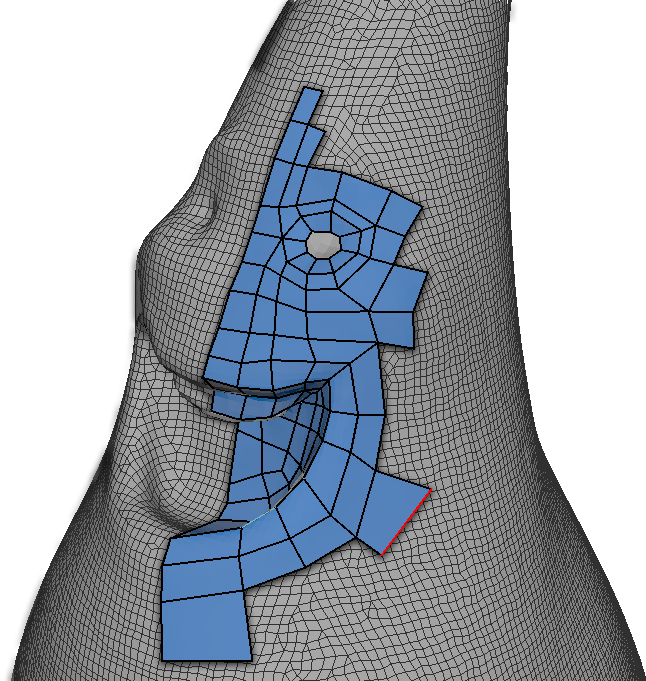
Week 04 Character Head Model Lab
Week 04 Character Head Model Lab:
The character’s body is complete but he lacks a head. In this lab we will put a head on its shoulders.
You will be graded on the following:
- Reference Accuracy
-
The model closely resembles the reference turnaround images.
-
- Geometry
-
Produce a clean mesh with few errors.
-
-
Topology
-
Strong gridflow that supports the form well.
-
-
Aesthetic
-
Excellent design that is appealing to look at.
-
Resources:
- Assignment Video Tutorials
- You may watch these tutorial videos below to help you complete your assignment.
- Assignment Lab Materials
- You may download the lab materials here: 3Dweek04LabMaterials.
Assignment Video Tutorials
Wait! Before you go!
Did you remember to?
- Read through this webpage
- Watch the videos
- Submit Week 04 Character Head Model Lab on Blackboard


 Click this link to download ZBrush Core Mini
Click this link to download ZBrush Core Mini